Lab Activity 15: Esters
Background:
An ester is an organic compound formed by the reaction of an alcohol with
an organic acid. An ester will hydrolyze unless the water formed in the
reaction is removed by dehydrating agent. In this investigation, you will
use sulfuric acid as the dehydrating agent in the general reaction:
H2SO4 |
||||||
ROH |
+ |
RCOOH |
------> |
RCOOR |
+ |
HOH |
Alcohol |
Organic Acid |
Ester |
Water |
Where R represents an organic radical such
as -CH3 or -C2H5.
The -COOH group is the functional group of an organic acid. The -OH group
is the functional group for alcohols.
Esters are useful as flavorings, aromatics, and solvents. The presence
of an ester is often noticed by a characteristic odor that is different
from either of the reactants. In this investigation, you will prepare
several familiar esters and try to identify them by their odors.
Purpose:
To prepare several esters and observe the mechanism for their general
reaction.
Materials:
| 125 ml Erlenmeyer flask | Iron ring | 60 cm piece of 5 mm glass tubing |
| 400 ml beaker | Wire gauze | Bunsen burner |
| Amyl (n-pentyl) alcohol | Ring stand | Concentrated (18 M) sulfuric acid |
| Salicylic acid crystals | Spatula | Stock glacial acetic acid |
| Methyl alcohol | Clamp | Cork or rubber stopper with hole to fit the Erlenmeyer flask and glass tubing |
| CAUTION: DO NOT HEAT ORGANIC CHEMICALS DIRECTLY WITH THE BURNER FLAME. ALWAYS HEAT ORGANIC CHEMICALS IN A WATER BATH, SINCE MANY ORGANIC CHEMICALS ARE VOLATILE AND FLAMMABLE. WEAR SAFETY GLASSES AND AN APRON THROUGHOUT THIS INVESTIGATION. | 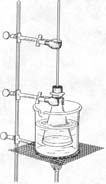 |
Figure 1: Setup |
Procedures:
1. Fit a cork with a 60 cm piece of glass
tubing. This tubing will serve as a condenser.
2. Set up a ring stand with ring and wire gauze. Half fill a 400-ml beaker
with water and place it on the wire gauze. Immerse a 125-ml Erlenmeyer
flask in the water bath and clamp it to the ring stand.
3. Add 5 ml of stock glacial acetic acid and 5 ml of methyl alcohol to
the flask. Then add 4 drops of concentrated sulfuric acid. Stopper the
flask with the cork you have fitted with the 60-cm piece of glass tubing
(See figure 1). Clamp the tubing to the ring stand.
4. Heat the water bath slowly until the mixture in the flask is gently
boiling. Make sure the heated reaction mixture does not rise above the
end of the glass tubing and spurt out. Continue to heat the water bath
for about 10 minutes.
5. Turn off the Bunsen burner and allow the mixture in the flask to cool.
Remove the glass tubing and note what has happened in the flask. Cautiously
smell the product of the reaction. Suggest a name for the ester that has
been formed.
6. Clean the Erlenmeyer flask and repeat procedures 1-5 using 5 ml of
amyl (n-pentyl) alcohol and 5 ml of glacial acetic acid. Remember to add
4 drops of concentrated sulfuric acid.
7. Clean the Erlenmeyer flask and repeat procedures 1-5 using 1 spatula
full of salicylic acid crystals and 5 ml of methyl alcohol. Remember to
add 4 drops of concentrated sulfuric acid.
SFP Home | Science Home | Barron's Web Site | Lab Index | WebChem